Start-ups slump as entrepreneurs brace for Brexit
- Number of new firms being started falls by 13% across the UK – with much sharper declines in many parts of England, Scotland and Northern Ireland
- Firms achieving sustained rapid growth and productivity gains remain a small minority
- ‘Warning signs’ highlight dangers for job creation from ongoing uncertainty around Brexit
The number of new start-ups in the UK fell sharply last year and established firms scaled back their growth ambitions due to Brexit uncertainty, according to new data looking at the health of the grassroots economy. The findings have emerged from the Enterprise Research Centre’s UK Local Growth Dashboard report, an annual publication that looks at a range of metrics charting the growth of small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which account for 99% of all firms in the UK.
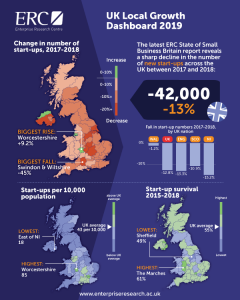
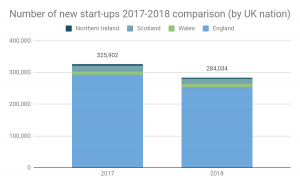
It found that in 2018 – the most recent period available in the ONS’ Business Structure Database – the number of new start-ups fell by nearly 42,000, representing a decline of 12.9% on the previous year for the UK as a whole (from 325,900 to 284,000).
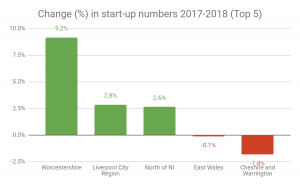
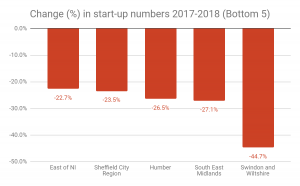
But in some parts of the country the fall was much sharper. In Northern Ireland as a whole the figure was 15% lower than in 2017, the biggest drop among the UK nations. Meanwhile in England, Swindon and Wiltshire saw the biggest absolute drop – with 45% fewer start-ups established. Just three areas saw an increase in start-ups – the North of Northern Ireland (+2.6%), Liverpool (+2.8%) and Worcestershire (+9.2%).
ERC researchers said the slowdown in new firm creation reflected the uncertainty around Brexit, and warned that the ongoing lack of clarity was also blunting growth ambitions in more established firms.
Other key findings from the UK Local Growth Dashboard report show that:
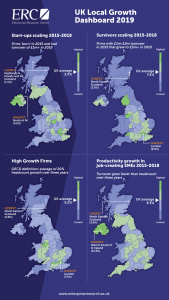
● A total of 284,000 new firms were started in 2018, while the three-year survival rate for start-ups stood at 55%. Start-up survival rates since 2015 were generally higher in the South of England and Northern Ireland, with many parts of the North of England and Midlands seeing a slight decline from the previous year.
● Among scale-ups, just 2% of new firms managed to grow their turnover to £1million or more within three years between 2015-18, with the highest proportion in the North of Northern Ireland (4.6%)
● For established firms with a turnover between £1million and £2million, 7.4% managed to grow above the £3million mark over three years. Again, London-based firms came top (9.5%), with significantly slower growth in more rural parts of England, as well as in Scotland, Northern Ireland and Wales.
● Fewer firms across the UK achieved ‘high growth’ status by growing their headcounts by an average of 10-20% each year for three years.
● The proportion of UK firms that succeeded in growing their productivity, with turnover increasing faster than headcount, slipped slightly to 8.3% in 2015-18, with Northern Ireland leading the pack (11.1%), followed by London, Cambridge and major city-regions in the North of England including Manchester, Leeds and Sheffield.
The ERC is the UK’s leading source of independent research insight on the growth of SMEs.
Mark Hart, ERC Deputy Director and Professor of Small Business and Entrepreneurship at Aston Business School, said:
“The latest Local Growth Dashboard analysis shows some clear warning signs about the health of the private sector economy in the UK. It’s particularly worrying that we’re seeing an absolute decline in the number of new businesses being started in the wake of the 2016 referendum.
“Budding entrepreneurs are clearly holding their breath waiting for some clarity about the outcome of Brexit, but if the trend continues we’ll see fewer jobs created by dynamic young firms.
“And while established firms are clearly still growing successfully in many parts of the country, it’s frustrating that productivity growth still seems to elude the vast majority.
“Taken together, it seems hard to avoid the conclusion that Brexit uncertainty is causing the grassroots economy to stutter. This may not yet have fed through to employment numbers, but policymakers need to be aware of the warning signs and create the certainty businesses are craving.”
ENDS
Notes to editors
1. Full report
A PDF copy of the Local Growth Dashboard is available on request. Please contact James Tout (details below)
2. Infographics (hi-res AI, PDF and PNG format versions available on request)
3. Charts
Number of new start-ups 2017-2018 comparison (by UK nation):
Change (%) in start-up numbers 2017-2018 (Top 5 and Bottom 5):
About the Enterprise Research Centre
ERC is the UK’s leading independent research institute on the drivers behind the growth and productivity of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). It is funded by the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS), the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC), Innovate UK, The Intellectual Property Office (IPO) and the British Business Bank (BBB). ERC is producing the new knowledge around SMEs that will allow us to create a business-friendly environment nationwide, grounded in hard evidence. We want to understand what makes entrepreneurs and firms thrive so we can spread the lessons from best practice and make the UK a more successful economy.
The Centre is led by Professors Stephen Roper of Warwick Business School and Mark Hart of Aston University, Birmingham. Our senior researchers are world-class academics from both Aston and Warwick Universities as well as from our partner institutions which include Imperial College, Queens University Belfast and the University of Strathclyde.